This research estimates $13bn of damages caused were attributable to anthropogenic global warming.
In August 2017 Hurricane Harvey, a category 4 cyclone, made landfall across the Greater Houston area. Its estimated cost ranges between 85 – 125 billion USD, the 2nd most expensive tropical cyclone in US history after adjustment for inflation.
In this paper Wehner and Sampson investigate the degree to which human induced climate change altered the flooding experienced during Hurricane Harvey, relative to if the climate had been in a ‘natural state’.
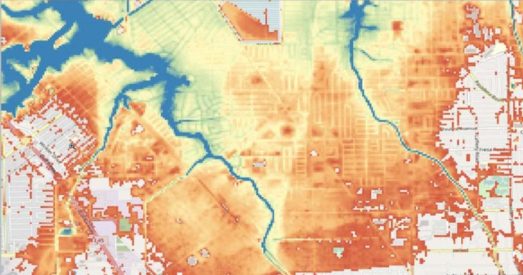
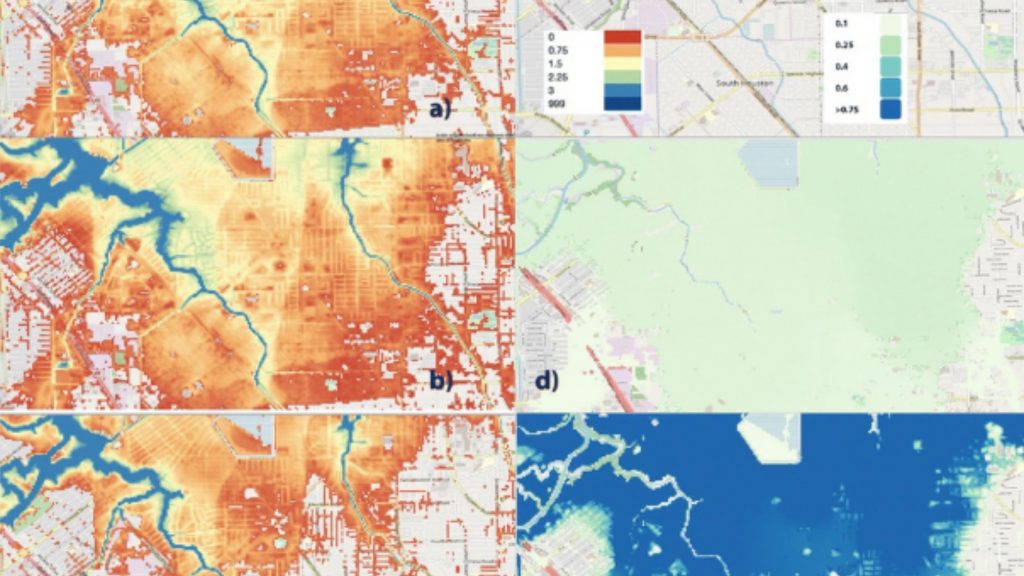
Using Fathom’s US flood model, they find non-linearities in the relation between precipitation increase due to climate change and the resultant flood inundation. In particular, increased flood volumes due to climate change in the most heavily flooded parts of Houston during Harvey were larger than the relative increase in precipitation.
Their research concludes that climate change increased the cost of Hurricane Harvey by 14% due to rising temperatures. This roughly translates to an estimated economic loss of $13 billion, attributable to anthropogenic global warming.